OpenID is a standard for user authentication. OpenID allow users to get access to different web services with the same digital identity. By using one OpenID we does not need to create different accounts for different web services.
An OpenID is a unique URL and authenticated by user's OpenID provider. The OpenID protocol does not work on a central authority for user's identity authentication. OpenID reduce frustration associated with maintaining multiple usernames and passwords and is the safer and easier method to joining new sites.
How to get OpenID:
How to login with OpenID?
1. When you visit a site that support OpenID and need authentication, you will see a form like this.
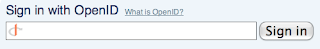 2. Enter your OpenID or your OpenID provider URL (for example yahoo.com) into the form.
2. Enter your OpenID or your OpenID provider URL (for example yahoo.com) into the form.
3. Your browser will send you to your OpenID provider login form.
4. Login to your OpenID provider site with your username and password.
5. Tell your provider that the original web site can use your identity. You are then sent back to the original website as authenticated user.
An OpenID is a unique URL and authenticated by user's OpenID provider. The OpenID protocol does not work on a central authority for user's identity authentication. OpenID reduce frustration associated with maintaining multiple usernames and passwords and is the safer and easier method to joining new sites.
How to get OpenID:
You may already have an OpenID. If you are using Google, Yahoo, Facebook etc , you does not need to create a new one. OpenID authentication is provided by several large websites. Several organizations either provide or accept OpenIDs, including Google, Facebook, Yahoo!, Microsoft, AOL, MySpace, Sears, etc.
How to login with OpenID?
1. When you visit a site that support OpenID and need authentication, you will see a form like this.
 2. Enter your OpenID or your OpenID provider URL (for example yahoo.com) into the form.
2. Enter your OpenID or your OpenID provider URL (for example yahoo.com) into the form.3. Your browser will send you to your OpenID provider login form.
4. Login to your OpenID provider site with your username and password.
5. Tell your provider that the original web site can use your identity. You are then sent back to the original website as authenticated user.
1 comment:
Good but this is not so common!
Post a Comment